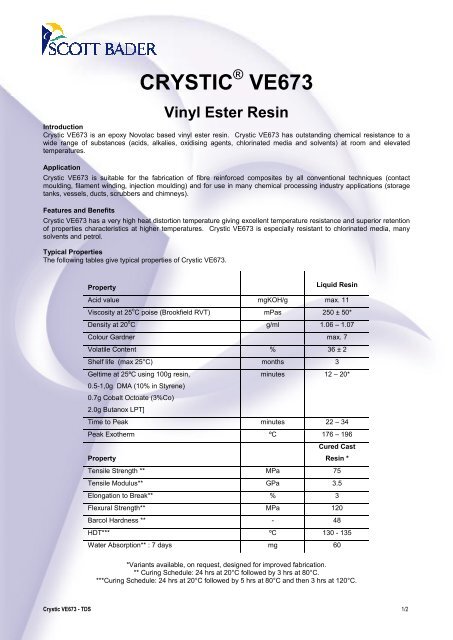
Vinyl ester resins are the binary resin systems containing a dimethacrylate monomer from which the cured material gains most of its properties and a reactive monomer such as styrene which acts as a reactive diluent and also takes part in the cross linking reaction.
Superior vinyl ester resin properties.
Vinyl ester resin or often just vinyl ester is a resin produced by the esterification of an epoxy resin with acrylic or methacrylic acids.
However these are relative and other resins or composites may be superior and more expensive.
Vinyl ester resins offer increased strength corrosion resistance and durability and are used in a wide variety of applications.
The resin properties and formulation are similar to derakane 470 36.
If improved durability and impact resistance is important then vinyl esters win over polyesters and again the build can be tailored to use the vinyl esters in those areas with higher impact probability.
Best solvent resistance of any styrenated epoxy vinyl ester resin improved thermal properties.
Flame retardant applications where translucency is required.
The diester product is then dissolved in a reactive solvent such as styrene to approximately 35 45 percent content by weight.
However when crosslinked vinyl esters are noticeably stronger and tougher than conventional polyester resins.
Use for equipment requiring superior corrosion resistance and thermal properties to standard flame retardant epoxy vinyl ester resins.
Advances in fire retardant materials 2008.
Epoxy novolak vinyl esters are particularly recommended for use in chlor alkali industry.
The vinyl groups refer to these ester substituents which are prone to polymerize.
Vinyl ester resins are easy to process and their physical properties in the uncured state are very similar to those of polyester resins.